Table of Contents
ToggleIn a world where healthcare is evolving faster than a caffeine-fueled nurse on a night shift, nurse education today stands at the forefront of this transformation. With the demand for skilled nurses skyrocketing, it’s not just about bandaging boo-boos anymore. Today’s aspiring nurses are diving into a sea of technology, evidence-based practices, and a sprinkle of compassion that could rival a Hallmark movie.
Gone are the days of dusty textbooks and chalkboards. Modern nursing education is a dynamic blend of online learning, hands-on simulations, and real-world experience. It’s like a reality show, but instead of drama, there’s critical thinking and patient care. As the healthcare landscape shifts, so does the training that prepares these unsung heroes to tackle the challenges ahead, ensuring they’re ready to save the day—one patient at a time.
Overview of Nurse Education Today
Nurse education today prioritizes skills and adaptability to meet the evolving demands of healthcare. Across the United States, nursing programs have shifted from purely theoretical frameworks to incorporate practical applications and technological advancements. Online learning platforms now complement traditional classroom settings, providing flexibility for students to manage their studies alongside personal responsibilities.
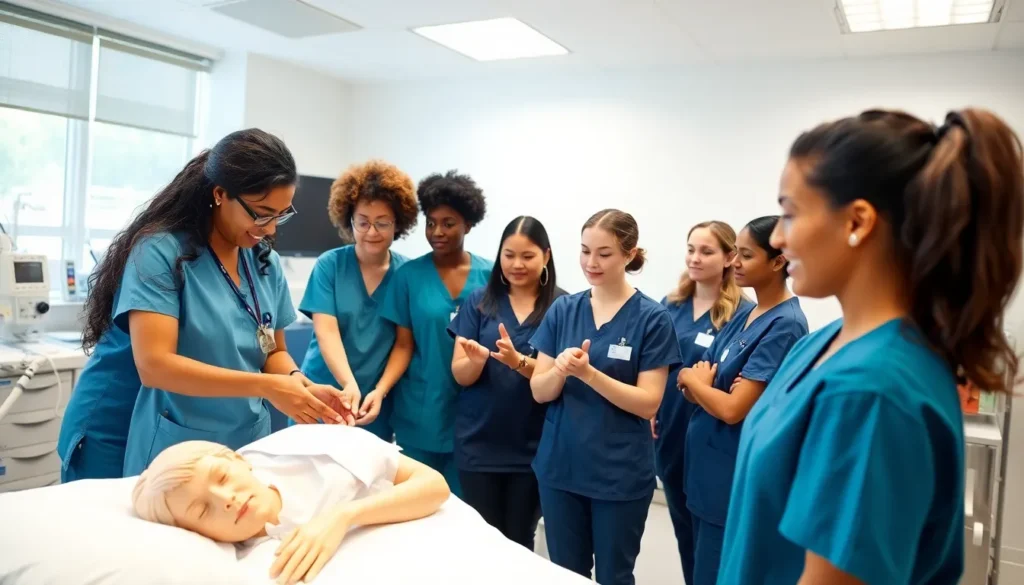
Hands-on simulations play a crucial role in preparing nursing students for real-world scenarios. These simulations offer experiential learning, enabling students to practice critical skills in a safe environment. Real-life clinical experiences follow, placing future nurses in actual healthcare settings to apply their knowledge.
Curriculums now focus on a holistic approach, emphasizing critical thinking and patient-centered care. In addition, interprofessional education fosters collaboration among healthcare professionals, preparing students for teamwork in diverse medical environments. Programs also address pressing issues like cultural competence and mental health care.
Statistical data highlights the growth in nursing education. In 2022, nursing schools in the U.S. saw an increase of 5% in enrollment, reflecting heightened interest in the profession. A transition towards Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degrees becomes evident as healthcare facilities increasingly prefer nurses with higher education.
As technology continues to advance, so does the integration of telehealth training in nursing programs. This prepares graduates for the remote care models that have emerged due to ongoing health challenges. Overall, nurse education today ensures a comprehensive foundation that equips future nurses to excel in dynamic healthcare systems.
Types of Nurse Education Programs

Nurse education offers various paths to accommodate different goals and learning preferences. Each program corresponds to specific roles within the healthcare system.
Associate Degree in Nursing
An Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) typically takes two to three years to complete. This program provides foundational nursing skills and knowledge, enabling graduates to pursue entry-level positions in hospitals and clinics. Many community colleges offer ADN programs, making them accessible to a broader audience. Successful completion prepares students for the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN), a crucial step for licensure. ADN graduates often find opportunities in patient care, offering essential support to nursing teams.
Bachelor of Science in Nursing
A Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) typically requires four years of study and emphasizes a more comprehensive nursing education. This program combines clinical practices with coursework in leadership, community health, and research. Hospitals increasingly prefer BSN graduates, as evidenced by the rise in enrollment, with a noted shift in healthcare facilities expecting higher educational qualifications. BSN programs foster critical thinking and offer advanced training to address complex patient needs. Graduates frequently engage in diverse roles, such as nurse educators or administrators, positioning themselves for career advancement.
Graduate Nursing Programs
Graduate nursing programs provide advanced education for nurses seeking specialization or leadership roles. Master’s degrees and Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) programs focus on areas such as nurse practitioner roles, clinical leadership, or nursing education. These programs require rigorous coursework and clinical practicums designed to develop expert-level skills. Enrollment in graduate programs has increased as the demand for specialized nursing practitioners grows, particularly in areas like mental health and geriatrics. Graduates often lead initiatives that improve patient care and contribute to healthcare policy.
Trends in Nurse Education
Nurse education continues to evolve, with significant trends shaping the landscape today.
Online Learning Opportunities
Online learning platforms offer flexible options for nursing students, enabling them to access courses at their convenience. These platforms often include interactive resources and multimedia materials, enhancing the learning experience. Many programs incorporate asynchronous formats, allowing students to study at their own pace while balancing personal and professional commitments. Moreover, a notable 53% of nursing programs have adopted hybrid models, blending online learning with in-person experiences, which increases accessibility. This shift supports diverse learning styles, making nursing education more inclusive for a broader range of students.
Simulation-Based Learning
Simulation-based learning plays a crucial role in preparing nursing students for real-world challenges. Realistic scenarios provide opportunities for hands-on practice, fostering clinical skills in a controlled environment. Students engage in high-fidelity simulations, which replicate emergency situations, enhancing their ability to respond effectively under pressure. Approximately 80% of nursing programs now integrate simulation experiences into their curricula, reflecting the increasing emphasis on practical skills. This method allows students to make mistakes and learn from them without risking patient safety, ultimately building confidence before entering actual clinical settings.
Challenges Facing Nurse Education
Nurse education faces several significant challenges that could impact the quality and availability of future healthcare professionals. These obstacles must be addressed to ensure the continued effectiveness of nursing programs.
Faculty Shortages
Faculty shortages present a critical issue in nurse education. Many nursing schools struggle to find qualified instructors, which limits the number of students they can accept. Data indicates that a lack of educators directly contributes to enrollment capacity constraints. In 2022, nearly 80,000 qualified applicants were turned away from nursing programs due to insufficient faculty. The aging workforce exacerbates this challenge as many experienced nurses retire. Schools must implement strategies to attract and retain nursing faculty to maintain educational standards and meet the rising demand for skilled nurses.
Student Enrollment and Retention
Student enrollment and retention rates significantly affect nursing programs. Recent statistics reveal a 5% increase in nursing school enrollment, showing growing interest in the profession. However, retention remains a challenge. Many students face financial and personal obstacles that hinder their educational journey. Institutions have started implementing support systems like tutoring and counseling, which assist students in overcoming these hurdles. Adapting curricula and providing flexible learning options can further enhance student engagement, ensuring that nursing programs continue to produce competent and dedicated professionals.
The Future of Nurse Education Today
Innovative teaching methods shape the future of nurse education. Programs increasingly rely on blended learning environments, integrating both online resources and traditional classroom experiences. A noticeable emphasis on simulation-based training prepares students for real-life clinical situations. Approximately 80% of nursing programs adopt high-fidelity simulations, allowing aspiring nurses to refine their skills safely and effectively.
Graduates enter the workforce with more than theoretical knowledge. Interprofessional education promotes collaboration among various healthcare disciplines, ensuring well-rounded training. Increased enrollment figures underscore the profession’s appeal; a 5% rise in nursing school attendance occurred in 2022. Preference for Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degrees continues to rise, driven by healthcare facilities’ desire for highly educated nurses.
Essentials like cultural competence and mental health training feature prominently in current curriculums. Students develop critical thinking abilities, preparing them to tackle complex patient care challenges. A supportive educational environment enhances retention, with institutions providing resources such as tutoring and counseling to address financial and personal hurdles.
Challenges persist, including a faculty shortage impacting student capacity for enrollment. Nearly 80,000 qualified applicants faced rejection in 2022, highlighting the need for more qualified educators. Solutions to these obstacles will shape the trajectory of nursing education.
Telehealth training prepares future nurses for evolving care models. The integration of technology in nurse education continues to adapt to ongoing health challenges, equipping graduates to thrive in diverse scenarios. Altogether, these advancements position nurse education to effectively meet the demands of modern healthcare systems.
Nurse education today is a dynamic landscape that adapts to the evolving needs of healthcare. With a focus on practical skills and technological integration, it prepares future nurses for real-world challenges. The commitment to interprofessional collaboration and cultural competence ensures that graduates are well-rounded and ready to provide patient-centered care.
Despite facing challenges like faculty shortages and retention issues, the innovative approaches in teaching methods promise a brighter future for nursing education. As enrollment continues to rise and the preference for advanced degrees grows, the profession’s appeal strengthens. The integration of telehealth training and simulation-based learning further enhances the readiness of nursing graduates, equipping them to thrive in an ever-changing healthcare environment.